OpenStage TDM FAQ
The Wiki of Unify contains information on clients and devices, communications systems and unified communications. - Unify GmbH & Co. KG is a Trademark Licensee of Siemens AG.
Revision as of 16:12, 28 November 2014 by Hoffmann.andreas (talk | contribs) (→Which trace-actions are available?)
In this OpenStage TDM you will find answers to frequently asked questions on the OpenStage T phone family, divided into various topics.
Contents
General
What documents are available for the OpenStage phones and where do I find them?
- All OpenStage phones are shipped with a printed document in multiple languages providing brief instructions regarding installation and operation. All the others are here on this Wiki.
How do I get an overview of the features of the OpenStage phones?
What are the default passwords?
- User Menu: no password
- Admin Menu: 123456
- Factory Reset: 124816
Administration
Diagnostics
Trace Guide Openstage TDM
What is a phone-trace?
- It is a capture of messages and activity states of the phone.
How can I get a phone-trace?
- The tracing is enabled via the Web interface, actions are then performed on the phone, during which the trace information is captured. When the desired actions have been performed, the captured trace information can be downloaded and viewed.
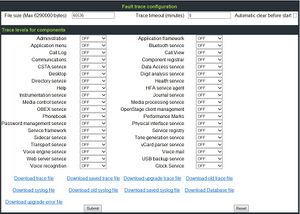
- For enabling tracing just enter the WBM, choose Administrator Pages and select Diagnostics. There you can enter the Fault trace configuration.
- The file size should be set to 500.000 bytes (768.000 bytes maximum). When the file size is reached, the phone save the trace file as old trace file and begins a new one. If the new one reaches the maximum file size, the old trace file will be replaced.
- You should only activate a few traces and use the function "Automatic clear before start" (old files will be deleted)
- The tracing is also reachable from the pbx (H4k-TSDM / H3k-Maintenance).
|
Tracing is only available on OpenStage T 60 or 80 devices at the TDM phone family. |
Which trace-actions are available?
- Administration
- This deals with the changing and setting of parameters within the phone database, from both the User and Admin menus.
- Application framework
- All applications within the phone e.g. Call view, Call log or Phonebook are run within the application framework. It is responsible for the switching: between different applications and bringing them into and out of focus as appropriate.
- Application Menu
- This is where applications to be run on the phone can be started and stopped.
- Call log
- This deals with the Call log application which displays the call history of the phone.
- Certificate management
- This service handles the verification and exchange of certificates for security and verification purposes. Nonrelevant for TDM.
- Component registrar
- This handles data relating to the type of phone e.g HFA/SIP Workpoint Hi/Workpoint Lo.
- Data Access service
- This service allows other services to access the data held within the phone database.
- Digit Analysis service
- This analyses and modifies digit streams which are sent and received by the phone e.g. canonical conversion.
- Directory service
- This performs a look up service for data in the phonebook, trying to match incoming and outgoing numbers with entries in the phonebook.
- Health service
- This monitors other parts of the phone for diagnostic purposes and provides a logging interface for the other services in the phone.
- Instrumentation service
- This is used by the Husim phone tester to exchange data with the phone for remote control, testing and monitoring purposes.
- Java
- Any Java applications run on the phone will be run in the Java sandbox controlled by the Java service.
- Media control service
- This service provides the control of media streams (voice, tones, ringing etc.) within the phone.
- Mobility service
- This handles the mobility feature whereby users can log onto different phones and have them configured to their own profile.
- Openstage Client Management
- This provides a means by which other services within the phone can interact with the database.
- POT service
- This service is supposed to take over control of basic telephony if the callview application fails.
- Physical interface service
- This handles any interactions with the phone via the keypad, mode keys, fixed feature buttons, clickwheel and slider.
- Service registry
- This keeps a record of all services which are currently running inside the phone
- Tone generation
- This service handles the generation of the tones and ringers on the phone.
- Voice engine
- This provides a switching mechanism for voice streams within the phone. It is also involved in QDC, Music on Hold and voice instrumentation.
- Application framework
- All applications within the phone e.g. Call view, Call log or Phonebook are run within the application framework. It is responsible for the switching :between different applications and bringing them into and out of focus as appropriate.
- Bluetooth Service
- This handles the Bluetooth interactions between external Bluetooth devices and the phone.
- Call view
- This handles the representation of telephony calls on the phone screen.
- Communications
- This is involved in the passing of call related information and signaling to and from the CSTA service.
- CSTA service
- Any CSTA messages, are handled by this service. CSTA messages are used within the phone by all services as a common call progression and control :protocol.
- Desktop
- The desktop service is responsible for the shared parts of the phone display. Primarily these are the status bar at the top of the screen and the FPK :labels.
- DLS Client management
- Interactions with the Deployment and licencing server are handled by this service. Nonrelevant for TDM.
- Help
- The help function is handled by this service.
- Journal service
- The Journal service is responsible for saving and retrieving call history information which is used by the Call log application.
- Media Processing service.
- This is a layer of software between the media control service and the tone generation and voice engine services. It is also involved in switching of :audio devices such as the handset and loudspeaker.
- OBEX service
- This is involved with Bluetooth accesses to the phone
- Phonebook
- This is responsible for the phonebook application within the phone.
- Password management service
- This is used to verify passwords used in the phone.
- Service framework
- This is the environment within which other phone services operate. It is involved in the starting and stopping of services.
- Sidecar service
- This handles interactions between the phone and any attached sidecars.
- Team Service
- This is primarily concerned with Keyset operation.
- Transport service
- The transport service provides the IP (LAN) interface between the phone and the outside world.
- Web Server service
- This provides the web access to the phone.
Web-based-Management (WBM)
At OpenStage T 60 and 80 phones only Trace-configuration is supported and possible in WBM.
User Data
|
Keep in mind that the user space is limited to 8 MB (total). Every picture, ringtone or phonebook entry will reduce the space left! |
Logo (Background picture)
How can I put my own company logo or background picture on the phone?
- This can be done by the pbx (H4k-TSDM / H3k-Maintenance).
What file types are supported?
- OpenStage 40 phones support BMP format (monochrome; 1 bit color depth).
- OpenStage 60/80 phones support PNG and JPG format, but PNG is the preferred file type because of the transparency feature.
- A logo file has to be resized to 144 x 32 pixel (OpenStage 40), 240 x 71 pixel (OpenStage 60) and(OpenStage 80)
- For a HowTo, see Administration Manual OpenStage HiPath 3000/4000, chapter 4.1.3
How can I return to the default logo?
- If you like to return to the standard logo (Siemens) feel free to download the respective file and deploy it to the phone.
- Below you can find all default logo files for OpenStage 80/60/40:
| OpenStage 60/80, Design: Silver Blue, PNG: | OpenStage 60/80, Design: Anthracite Orange, PNG: | OpenStage 40, BMP: |

|

|
|
Can I show a logo with key labelling help?
- In some situations it may be helpful to have a verbal reference of the keys available. This can be very easily reached, if you download a key-Reference logo on your phone.
| OpenStage 60/80, PNG: | OpenStage 40, zipped BMP: |
Screensaver
Can I use my own pictures for the screensaver slideshow?
- Yes, this is possible. Easiest way doing this, is with the help of the OpenStage Manager tool. It transfers all the pictures to the phone, makes them fit best on the screen and can help saving memory.
Which formats are supported?
How many pictures can be downloaded?
- This depends on the memory usage for other user data (eg. phonebook entries, ringer tones). The total memory available is limited to 8 MB.
Local phonebook
Is it possible to synchronize my Outlook contacts with OpenStage?
- This can be done with the OpenStage Manager.
- You need following Canonical Dial settings
- This is a sample for a client on number +49 2302 98038-11
- Local country code: 49
- National prefix digit: 0
- Local national code: 2302
- Min. local number length: 5
- Local enterprise node: 98038
- PSTN access code: 0
- International access code: 00
- and you need following Canonical Dial Lookup settings
- local code: 98038
- international code: +49230298038
How can I get my mobile phone contacts to OpenStage?
- Using the Bluetooth functionality of OpenStage 60 and 80. Via Bluetooth you can easily transfer a contact as a vCard (if supported by the mobile phone).
Ringer tones
What file types are supported?
- In general, WAV and MIDI files are supported on all 4 phone types. Additionally, OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files.
Is there a suggestion for MP3 files?
- OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files from 32 kbit/s up to 320 kbit/s (stereo and mono). Because of a limitation of the space available (8 MB in total), the following is suggested:
- - mono instead of stereo sound
- - a constant bitrate between 64 and 96 kbit/s
- - a maximum length of 15 seconds per file
- See the following table for estimated file size
64 kbit/s (mono) 80 kbit/s (mono) 96 kbit/s (mono) Length 5 seconds 40 KB 50 KB 60 KB Length 10 seconds 80 KB 100 KB 120 KB Length 15 seconds 120 KB 150 KB 180 KB
See also
- OpenStage - the portal page of the OpenStage telephone family
- OpenStage Training - easy learning to use your feature-rich enterprise phone
- OpenStage Manager - feature description of the PC application for OpenStage
- OpenStage power supply and PoE classes - required power supply and PoE classes of phones and accessories
- OpenStage Hardware Changes and necessary Software Versions - comparative table of supported hardware versions
- OpenStage Bluetooth - OpenStage 60/80 Bluetooth feature information
- OpenStage Accessories - Add-On devices, Adapters and Accessories
- OpenStage Main Navigation - comparative information about the main navigation elements