OpenStage SIP FAQ
The Wiki of Unify contains information on clients and devices, communications systems and unified communications. - Unify GmbH & Co. KG is a Trademark Licensee of Siemens AG.
In this OpenStage SIP you will find answers to frequently asked questions on the OpenStage SIP phone family, divided into various topics.
Read more about new or hidden SIP features.
Contents
- 1 General
- 2 Administration
- 3 Web-based-Management (WBM)
- 4 User Data
- 5 Platform Support
- 6 See also
General
What documents are available for the OpenStage phones and where do I find them?
- All OpenStage phones are shipped with a printed document in multiple languages providing brief instructions regarding installation and operation. All the others are here on this Wiki.
How do I get an overview of the features of the OpenStage phones?
- You will get a quick overview of the features in the corresponding OpenStage datasheets, which you can alternatively view under http://www.siemens.de/hipath > Downloads > Data sheets.
- Another short overview is available on the OpenStage page.
What are the default passwords?
- User Menu: no password
- Admin Menu: 123456
- Factory Reset: 124816
Security Advisory: ensure that the default passwords (both user and admin access) are changed to individual complex passwords when a phone gets into operation. This is especially important in deployment scenarios where remote administration via WBM (web-based management) is enabled.
How can I invoke a soft-Restart?
How can I invoke a factory reset?
Administration
Diagnostics
Trace Guide Openstage SIP
How can I monitor the phones IP traffic?
- Best way, just configure the PC-port of your OpenStage phone as a mirror of the first one and trace phones IP/SIP traffic with a network tracer running on the PC connected to the phones PC-port.
What is a phone-trace?
- It is a capture of messages and activity states of the phone.
How can I get a phone-trace?
- The tracing is enabled via the Web interface, actions are then performed on the phone, during which the trace information is captured. When the desired actions have been performed, the captured trace information can be downloaded and viewed.
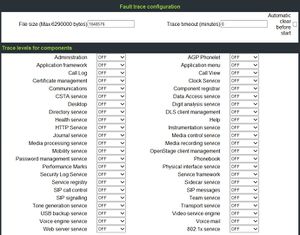
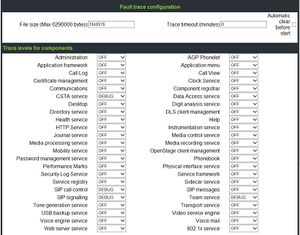
- The file size should be set to 2.500.000 bytes. When the file size is reached, the phone save the trace file as old trace file and begins a new one. If the new one reaches the maximum file size, the old trace file will be replaced.
- You should only activate a few traces and use the function "Automatic clear before start" (old files will be deleted)
Which trace-actions are available?
- Administration
- This deals with the changing and setting of parameters within the phone database, from both the User and Admin menus.
- Application framework
- All applications within the phone e.g. Call view, Call log or Phonebook are run within the application framework. It is responsible for the switching :between different applications and bringing them into and out of focus as appropriate.
- Application Menu
- This is where applications to be run on the phone can be started and stopped.
- Bluetooth Service
- This handles the Bluetooth interactions between external Bluetooth devices and the phone.
- Call log
- This deals with the Call log application which displays the call history of the phone.
- Call view
- This handles the representation of telephony calls on the phone screen.
- Certificate management
- This service handles the verification and exchange of certificates for security and verification purposes.
- Communications
- This is involved in the passing of call related information and signaling to and from the CSTA service.
- Component registrar
- This handles data relating to the type of phone e.g HFA/SIP Workpoint Hi/Workpoint Lo.
- CSTA service
- Any CSTA messages, are handled by this service. CSTA messages are used within the phone by all services as a common call progression and control :protocol.
- Data Access service
- This service allows other services to access the data held within the phone database.
- Desktop
- The desktop service is responsible for the shared parts of the phone display. Primarily these are the status bar at the top of the screen and the FPK labels.
- Digit Analysis service
- This analyses and modifies digit streams which are sent and received by the phone e.g. canonical conversion.
- Directory service
- This performs a look up service for data in the phonebook, trying to match incoming and outgoing numbers with entries in the phonebook.
- DLS Client management
- Interactions with the Deployment and licencing server are handled by this service.
- Health service
- This monitors other parts of the phone for diagnostic purposes and provides a logging interface for the other services in the phone.
- Help
- The help function is handled by this service.
- Instrumentation service
- This is used by the Husim phone tester to exchange data with the phone for remote control, testing and monitoring purposes.
- Java
- Any Java applications run on the phone will be run in the Java sandbox controlled by the Java service.
- Journal service
- The Journal service is responsible for saving and retrieving call history information which is used by the Call log application.
- Media control service
- This service provides the control of media streams (voice, tones, ringing etc.) within the phone.
- Media Processing service.
- This is a layer of software between the media control service and the tone generation and voice engine services. It is also involved in switching of :audio devices such as the handset and loudspeaker.
- Mobility service
- This handles the mobility feature whereby users can log onto different phones and have them configured to their own profile.
- OBEX service
- This is involved with Bluetooth accesses to the phone
- Openstage Client Management
- This provides a means by which other services within the phone can interact with the database.
- Phonebook
- This is responsible for the phonebook application within the phone.
- POT service
- This service is supposed to take over control of basic telephony if the callview application fails.
- Password management service
- This is used to verify passwords used in the phone.
- Physical interface service
- This handles any interactions with the phone via the keypad, mode keys, fixed feature buttons, clickwheel and slider.
- Service framework
- This is the environment within which other phone services operate. It is involved in the starting and stopping of services.
- Service registry
- This keeps a record of all services which are currently running inside the phone
- Sidecar service
- This handles interactions between the phone and any attached sidecars.
- SIP call control
- This is contains the call model for the phone and is associated with telephony and call handling.
- SIP Messages
- This traces the SIP messages which are exchanged by the phone. Activating the SIP messages trace requires a reboot of the device
- SIP signalling
- This is involved in the creation and parsing of SIP messages and communicates directly with the SIP stack.
- Team Service
- This is primarily concerned with Keyset operation.
- Tone generation
- This service handles the generation of the tones and ringers on the phone.
- Transport service
- The transport service provides the IP (LAN) interface between the phone and the outside world.
- vCard parser service
- This trace is for sending/recieving vCards via the Bluetooth interface.
- Voice engine
- This provides a switching mechanism for voice streams within the phone. It is also involved in QDC, Music on Hold and voice instrumentation.
- Voice mail
- This trace monitors the integrated Voice mail application of the phone.
- Web Server service
- This provides the web access to the phone.
- USB Backup service
- This is for the backup/restore feature via USB devices.
- Voice recognition
- The Voice recognition service is for the voice dialling feature
- 802.1x service
- This is for port security (802.1x)
Error codes
When do I see the error codes?
- Whenever a phone is unable to register it brings up a message (No telephony possible) together with an error code. The error code helps you to identify where the problem is.
List of error codes
Problem Detail Error code Network Problem No network connection LI Not Initialised Waiting for data I Unable to use LAN 802.1x error LX Unable to use LAN Physical connection missing LP Unable to Register Server timeout RT Unable to Register Server failed RF Unable to Register Authentication failed RA Unable to Register No number configured RN Unable to Register No server configured RS Unable to Register No registrar configured RG Unable to Register No DNS domain configured RD Unable to Register Rejected by server RR Unable to Register No phone IP address set RI Survivability Backup route active B Survivability Backup not configured RS Survivability Backup timeout RT Survivability Backup authentication failed RA
Codecs
What codecs are supported with OpenStage?
- - G.711 (A-Law and u-Law)
- - G.729AB (OpenStage can decode G.729 and G.729A but encodes only with G.729A)
- - G.722 wideband codec
Compatibility
Can I move a Mobile User between an optiPoint and an OpenStage telephone and vice versa?
Cross mobility is released with the following restriction: Mobility between OpenStage and optiPoint410/420 phones is released with OpenStage SW version V2R0.16.0 and higher but please take notice of some minor restrictions/ details to be taken into account (see information below). With OpenStage SW version V2R0.16.0 and higher the "mobility log-on/ log-off" is released for mobile users logging in or off from any OpenStage SIP to optiPoint 410/420 SIP and vice versa. However: There are a few details and shortcomings to be taken into account when it comes to creating a mobile user in DLS and the interworking of default settings especially for multi-line appearance (position of the keys while using mobility and the key layout). In order to both understand and gain an overview on details to be taken into account please refer to the "Cross Mobility" document
SIP Mobility User - optiPoint and OpenStage Regression Test.
LDAP
|
Accessing the LDAP server is only available on OpenStage 60 or 80 devices. |
What is the purpose of a LDAP template?
See also: LDAP on OpenStage
- A LDAP template has to be downloaded to the phone via local phone menu or WBM, because it contains necessary information about the search attributes and the location of all user data inside the directory.
Where do I get the template from?
- It is a plain txt file and must fit your directory environment. The configuration for a Microsoft Active Directory would look like this:
- OpenStage LDAP TEMPLATE (v.1)
- SEARCHBASE="OU=Users,DC=microsoft,DC=com"
- ATTRIB01="sn"
- ATTRIB02="givenName"
- ATTRIB03="telephoneNumber"
- ATTRIB04="otherTelephone"
- ATTRIB05="mobile"
- ATTRIB06="homePhone"
- ATTRIB07="company"
- ATTRIB08="department"
- ATTRIB09="l"
- ATTRIB10="title"
- ATTRIB11="mail"
- EOF
- If your are not using a Microsoft AD, you have to adjust the template:
- OpenStage LDAP TEMPLATE (v.1)
- SEARCHBASE="OU=Users,DC=yourdomain,DC=toplevel"
- ATTRIB01="Last Name"
- ATTRIB02="First Name"
- ATTRIB03="Business phone numer 1"
- ATTRIB04="Business phone numer 2"
- ATTRIB05="Mobile phone number"
- ATTRIB06="Home phone number"
- ATTRIB07="Company"
- ATTRIB08="Address 1"
- ATTRIB09="Address 2"
- ATTRIB10="Job function"
- ATTRIB11="E-Mail address"
- EOF
Configuration at the phone.
- Besides the template, add the following information in the admin menu of the OpenStage SIP phone: Admin --> Local functions --> Directory Settings
- LDAP server address
- LDAP server port
- LDAP authentication (if Simple, add authentication information below)
Restrictions
- Up to now, the address is saved in one single field, which makes it difficult to search for a complete address. It is up to the administrator to which subject of the Directory the address fields are matched with.
Web-based-Management (WBM)
- With the WBM are changes in settings possible, which can also be performed in the phone-menu, but you have the adventage that you needn't be in front of the phone.
- Trace-configuration is only possible in WBM.
User Data
|
Keep in mind that the user space on
Every picture, ringtone or phonebook entry will reduce the space left! |
File limits
Ring-tones
- File size: 1000000 Bytes max per file
- Number of files: no limit (memory related)
Screensavers
- File size: 300000 Bytes max per file
- Number of files: no limit (memory related)
Picture clips
- File size: 300000 Bytes max per file
- Number of files: no limit (memory related)
MOH
- File size: no limit
- Number of files: 1
LDAP Template
- File size: no limit
- Number of files: 1
USB support to backup/restore user data
Which OpenStage SIP phones provide an USB port and what kind of USB port do they have?
The OpenStage 60 SIP and OpenStage 80 SIP provide an USB master port.
What can I connect to this port?
You can connect an USB memory stick to back-up and restore personal data, like phonebook, ringer tones and pictures (for details see below). All data you find under Settings ⇒ User (no admin data).
The hardware of the OpenStage SIP phones does not allow for connecting a USB hub (e.g. acoustic unit). This might be supported in a future release.
What USB features can I use?
- Backup of data into USB (with a password, and then it is encrypted)
- Restore of data from USB (with a password, and then it is decrypted)
- Encryption/Decryption of the backup data (storing on USB memory stick and loading data from USB memory stick is encrypted)
- Replace backup
- Delete backup
- HotPlug device
- ColdPlug device
- Getting product name (the phone is told the USB device name)
Can I store more than one phone configuration on an USB memory stick?
- Yes. It depends only on the size of memory of the USB memory stick.
Logo (Background picture)
How can I put my own company logo or background picture on the phone?
- This can either be done by local phone menu or Webbased management. The logo file has to be placed on a FTP server, where the phone can download it.
What file types are supported?
- OpenStage 40 phones support BMP format (monochrome).
- OpenStage 60/80 phones support PNG and JPG format, but PNG is the preferred file type because of the transparency feature.
- A logo file has to be resized to 144 x 32 pixel (OpenStage 40), 240 x 70 pixel (OpenStage 60) or 480 x 142 pixel (OpenStage 80)
- For a HowTo, see
 Administration Manual OpenStage OpenScape Voice, chapter 4.2.
Administration Manual OpenStage OpenScape Voice, chapter 4.2.
How can I return to the default logo?
- If you like to return to the standard logo (Siemens) feel free to download the respective PNG file and deploy it to the phone.
- Below you can find all default logo files for OpenStage 80/60/40:
- File:80 Crystal Sea.pngOpenStage 80, Design: Crystal Sea (download)
- File:60 Crystal Sea.pngOpenStage 60, Design: Crystal Sea (download)
- File:80 Warm Grey.pngOpenStage 80, Design: Warm Grey (download)
- File:60 Warm Grey.pngOpenStage 60, Design: Warm Grey (download)
-
 40_Standard_logo (bmp file)
40_Standard_logo (bmp file)
Logo to show key labelling
- In some situations it may be helpful to have a verbal reference of the keys availble. This can be very easily reached, if you download a key-Reference logo on your phone.
-
 OpenStage 80, Design: both (download)
OpenStage 80, Design: both (download)
-
 OpenStage 60, Design: both (download)
OpenStage 60, Design: both (download)
-
 40_key_reference_logo (bmp file)
40_key_reference_logo (bmp file)
Screensaver
Can I use my own pictures for the screensaver slideshow?
- Yes, this is possible. Easiest way doing this, is with the help of the OpenStage Manager tool. It transfers all the pictures to the phone, makes them fit best on the screen and can help saving memory.
Which formats are supported?
How many pictures can be downloaded?
- This depends on the memory usage for other user data (eg. phonebook entries, ringer tones). The total memory available is limited to 8 MB.
Local phonebook
Is it possible to synchronize my Outlook contacts with OpenStage?
- This can be done with the OpenStage Manager.
How can I get my mobile phone contacts to OpenStage?
- Using the Bluetooth functionality of OpenStage 60 and 80. Via Bluetooth you can easily transfer a contact as a vCard (if supported by the mobile phone).
Ringer tones
What file types are supported?
- In general, WAV and MIDI files are supported on all 4 phone types. Additionally, OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files.
Is there a suggestion for MP3 files?
- OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files from 32 kbit/s up to 320 kbit/s (stereo and mono). Because of a limitation of the space available (8 MB in total), the following is suggested:
- - mono instead of stereo sound
- - a constant bitrate between 64 and 96 kbit/s
- - a maximum length of 15 seconds per file
- See the following table for estimated file size:
64 kbit/s (mono) 80 kbit/s (mono) 96 kbit/s (mono) Length 5 seconds 40 KB 50 KB 60 KB Length 10 seconds 80 KB 100 KB 120 KB Length 15 seconds 120 KB 150 KB 180 KB
How can I download my own ringer melodies to the OpenStage 60/80 phones?
- This can be done by using the OpenStage Manager. As an instance of ringtones, several MP3 files can be found here.
How can I download my own ringer melodies to the OpenStage 15/20/40 phone?
- This can be done via FTP or Deployment Service. If you want to replace it, you need to download a new file with the same name. Of course a factory resets turns the phone in the original state and eleminates individual downloaded ringer files.
- MIDI files are used from SIP V2 R1 onward instead of WAV files.
- The original OpenStage 15, 20 and 40 WAV Ringerfiles can be downloaded here:
 OS_Ringtones_15_20_40
OS_Ringtones_15_20_40
Music-On-Hold (MoH)
What file types are supported?
- In general, WAV and MIDI files are supported on all 4 phone types. Additionally, OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files.
Is there a suggestion for MP3 files?
- OpenStage 60 and 80 can play MP3 files from 32 kbit/s up to 320 kbit/s (stereo and mono). Because of a limitation of the space available (8 MB in total), the following is suggested:
- - mono instead of stereo sound
- - a constant bitrate between 64 and 96 kbit/s
- - a maximum length of 15 seconds
- - there can only be one single Music on Hold file at once
- See the following table for estimated file size
64 kbit/s (mono) 80 kbit/s (mono) 96 kbit/s (mono) Length 5 seconds 40 KB 80 KB 120 KB Length 10 seconds 50 KB 100 KB 150 KB Length 15 seconds 60 KB 120 KB 180 KB
How can I download my own Music on Hold to the phone?
- This can be done by using the OpenStage Manager. Only one file can be downloaded, because there is no selection of files available.
How can I get back to the factory default Music?
- The file can be downloaded from here:
 OpenStage Default MoH.
OpenStage Default MoH.
Use of Bluetooth headset with OpenStage
How can I automatically reconnect my BT headset after I have lost connection ?
OpenStage offers the bluetooth "headset profile" to support bluetooth headsets. However there are some bluetooth headsets on the market that also use the "hands-free profile" especially e.g. to automatically reconnect a headset after the headset has lost the connection. The "hands-free profile" will be implemeted in OpenStage but is currently not available.
How can I check if my headset is connected?
On the display of your OpenStage phone, right next to the bluetooth symbol you see a small additional symbol that looks like two waves.
What is the current work-around?
For incoming calls there is no problem because OpenStage reconnects the Bluetooth headset automatically when a call comes in. Thus there is only a need for a workaround for outgoing calls: If you want to make a call using the headset you can push the on/off-hook key of the headset once before dialling. This reconnects the headset again and you don't have to go into the menu structure of the OpenStage to do it.
Platform Support
How can I connect my OpenStage phone to an Asterisk system?
See OpenStage and Asterisk for further details.
See also
- OpenStage - the portal page of the OpenStage telephone family
- OpenStage Training - easy learning to use your feature-rich enterprise phone
- OpenStage Manager - feature description of the PC application for OpenStage
- OpenStage power supply and PoE classes - required power supply and PoE classes of phones and accessories
- OpenStage Hardware Changes and necessary Software Versions - comparative table of supported hardware versions
- OpenStage Bluetooth - OpenStage 60/80 Bluetooth feature information
- OpenStage Accessories - Add-On devices, Adapters and Accessories
- OpenStage Main Navigation - comparative information about the main navigation elements