Difference between revisions of "OpenScape Voice"
The Wiki of Unify contains information on clients and devices, communications systems and unified communications. - Unify GmbH & Co. KG is a Trademark Licensee of Siemens AG.
(→Performance features) |
(→Flat VLAN Design) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
=== Flat VLAN Design === | === Flat VLAN Design === | ||
| − | In a flat VLAN design, the VLANs are extended from one | + | In a flat VLAN design, the VLANs are extended from one OpenScape Voice node to the other. In case of failure of an active node, the IP addresses of this node is transfered to the other. A drawback of this design is, that high redundancy can only be achieved when using redundant layer 2 networks with the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spanning_tree_protocol Spanning Tree Protocol] being used to remove loops from the network. However, note, that Spanning Tree problems can lead to 100% network load and to the unavailibility of both HiPath 8000 nodes. Also, Spanning Tree problems are easy to troubleshoot. We recommend to a Split Subnet design with a Spanning Tree less design if possible. |
=== Split Subnets === | === Split Subnets === | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 13 July 2009
OpenScape Voice is an IP softswitch for large and very large companies up to 100,000 users. OpenScape Voice was formerly known as HiPath 8000.
Contents
Performance features
The OpenScape Voice is a native SIP-based Real-Time IP System that is ideal for both large and very large enterprises and for managed service providers. Designed for data center deployment, OpenScape Voice fits perfectly into the IT world. It allows companies to simply and cost-effectively integrate converged voice, multi-media and multi-modal services.
System architecture
- Software: Linux based
- Hardware: IBM e-Series with two Intel Xeon CPUs
Applications and Devices
The following devices can be connected to OpenScape Voice:
- OpenStage SIP phones:
- optiPoint 410/420 S phones:
- optiPoint WL2 professional S
- optiPoint 150 S
- optiClient 130 S
Administration and Service
Networking scenarios
Networking Scenarios are discussed in Detail in the Edoku HiPath 8000 Network Planning Guide (non-public). However, note, that at least the VLAN design will be changed soon. Here, we document the new proposal.
Flat VLAN Design
In a flat VLAN design, the VLANs are extended from one OpenScape Voice node to the other. In case of failure of an active node, the IP addresses of this node is transfered to the other. A drawback of this design is, that high redundancy can only be achieved when using redundant layer 2 networks with the Spanning Tree Protocol being used to remove loops from the network. However, note, that Spanning Tree problems can lead to 100% network load and to the unavailibility of both HiPath 8000 nodes. Also, Spanning Tree problems are easy to troubleshoot. We recommend to a Split Subnet design with a Spanning Tree less design if possible.
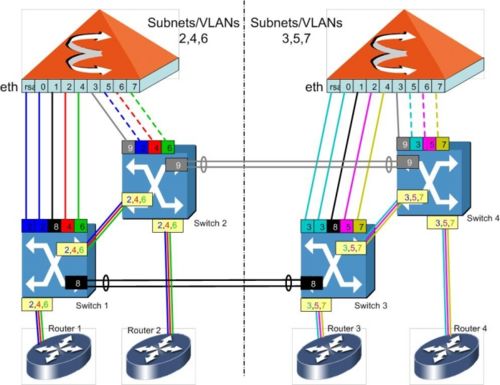
Split Subnets
With the Split Subnets design, all VLANs except the cluster interconnect are local to one OpenScape Voice node only. See below a proposal of the VLAN design, which can not be found in the Edoku yet (version 2.2, issue 2):
Loop-less (Spanning Tree-less) VLAN Design for a OpenScape Voice Split Subnet Design.
Note, that the Routers SHOULD NOT be attached redundantly. If e.g. Router 1 is attached to Switch 1 and Switch 2 with VLANs 2, 4 and 6 on both links, a layer 2 loop would be created (Router 1 -- Switch 1 -- Switch 2 -- Router 1). To resolve this, we will need Spanning Tree on the Switches as well as on the Router. However, the need for Spanning Tree is to be avoided and Spanning Tree should only be switched on the Switches for decreasing the impact on any erroneous miscabling.