optiPoint application module Programming WML applications
The Wiki of Unify contains information on clients and devices, communications systems and unified communications. - Unify GmbH & Co. KG is a Trademark Licensee of Siemens AG.
| |
This article or section is currently under construction. In order to avoid editing conflicts, please wait until this message is removed or contact the author (Horst.reinelt 16:35, 14 August 2006 (CEST)). |
The target group for this guide to program WML applications are developers creating WML applications for the optiPoint application module.
The guide covers all elements/tags that are part of the WML 1.3 specification. It describes the individual WML elements, their attributes and their interpretation by the WAP browser application as far as it is relevant for the WAP developer.
Of course, this guide does not supersede a WML training manual.
Contents
Technical Browser Properties
This chapter specifies the relevant physical properties of the optiPoint application module.
Maximum Data Volume
The following restrictions have to be taken into account when developing WAP pages for the optiPoint application module:
- The individual cards should not exceed 15 kilobytes (including graphics).
- A deck should not exceed 80 kilobytes (including graphics).
The optiPoint application module was developed for a wired LAN environment and the HTTP transfer protocol. If the browser is connected via a WAP gateway, WSP can be used instead of HTTP. In this case please consider that some gateways restrict the data volume transferred via WSP. Please also note that WAP gateways usually compile WML pages (i.e. compress them to a binary format). This format considerably reduces the data volume.
Display
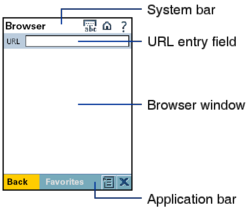
If the browser is used, the display is divided into a system bar, a URL entry field, the browser window for the WAP content and the application bar with symbols to open the context menu an exit the browser.
The display has a total size of 320 (height) by 240 (width) pixels. If the content is bigger, please take into account that the two scroll bars take a certain part of the available display size. As soon as a vertical scroll bar is shown, the visible width of the browser window is reduced so much that a horizontal scroll bar is also displayed at the bottom of the screen.
If you want to fill the display with a maximum size graphic without triggering the display of scroll bars, rectangles of 230 (width) by 221 (height) pixels or 234 (width) by 192 (height) pixels are available. The difference is due to different threshold values that trigger the generation of scroll bars. In detail, the scroll bar behaviour is as follows: If the maximum height is exceeded, both vertical and horizontal scroll bars are displayed; if only the maximum width is exceeded and the height is smaller than or equals 192 pixels, only a horizontal scroll bar is generated.
The maximum scope for text content is 9 lines (normal font and size). Starting with the 10th line, both a vertical and a horizontal scroll bar are displayed. If a string of characters that cannot be syllabicated exceeds the display width, two things happen: The display is expanded by generating a horizontal scroll bar, and the string of characters is wrapped right in front of the character that exceeds the maximum length.
Using the Browser
The following explains how to use the browser. For detailed information refer to the Operating Manual.
Keyboard and Touchscreen
An alphanumeric keyboard and a touchscreen keypad are available for navigation and data entry. Before you can enter e.g. a URL into the address bar or data into an entry field, the field has to be activated using the touchscreen. Also, task or form elements can only be selected via the context menu, i.e. through the touchscreen.
Certain characters have to be entered via the touchscreen keypad which contains the complete character set. Some special characters (e.g. the * and #) are only available within a submenu of the touchscreen keypad.
Touchscreen Keypad
Starting and Closing the Browser
In the initial state, the optiPoint application module displays the start menu.
| Step by Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Select the browser symbol using the touchscreen or the navi key. Once the browser symbol is selected, a second click on the symbol using the touchscreen or the confirmation using the navi key starts the browser, displaying the pre-defined start page. | |
| You can close the browser by clicking on the cross symbol.
By activating the home symbol you return to the start menu and can change to another application. In this case, the browser is not closed, i.e. the browser retains its current status. |
Context Menu
Using the context menu (symbol in the application bar) you can:
- access the browser’s homepage
- manage the favorites or add the current page to the favorites
- reload the page, i.e. the deck
- set user name/password combinations for access to the gateway or proxy
- use Options to access the softkeys generated via WML
Data Formats / MIME Types
To WAP-enable a web server, the following MIME types have to be defined:
| Filename extension | MIME Type | File Contents |
|---|---|---|
| .wml | text/vnd.wap.wml | WML document in plain text format |
| .wmlc | application/vnd.wap.wmlc | WML document in binary format |
| .wbxml | application/vnd.wap.wbxml | WML document in binary format |
| .wbmp | image/vnd.wap.wbmp | Image in WBMP format (Wireless Bitmap) |
| .wmlsc | application/vnd.wap.wmlscriptc | WMLScript in compiled format |
Data Formats
Due to its compression, the binary format allows for faster transfer of XML files.
One of the reasons for the considerably smaller file size is that WML elements are represented by defined byte values; in plain text files these are represented as strings, resulting in increased redundancy. The compilation from plain text to binary format can be done in the WAP Gateway or in a separate application. A useful tool is e.g. the WBXML Library.
The filename extensions .wmlc and .wbxml can be used alternatively for the same binary format.
Server Configuration
You can use one of the standard web servers, e.g. Apache or Microsoft IIS to provide WML pages. In addition, dynamic WAP pages can be generated using the same tools as dynamic HTML pages: ASP, CGI/Perl, PHP, JSP, etc.
HTTP
HTTP Header
If you want to adapt a WAP application for the optiPoint application module’s browser, it is useful to know the information sent from the client to the server.
The following table shows the data sent to the server in the HTTP header. To show a typical scenario, the header data display the corresponding CGI environment variable.
| Environment Variable | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP_ACCEPT | text/vnd.wap.wml, application/vnd.wap.wmlc, application/vnd.wap.wbxml, application/vnd.wap.wmlscriptc | List of the MIME types accepted by the browser. |
| HTTP_ACCEPT_CHARSET | utf-8, utf-16, iso-8859-1 | List of the character codes accepted by the browser. |
| HTTP_USER_AGENT | SIE-OP410 | Browser type |
| REMOTE_ADDR | IP Address | IP address of the terminal device the application module is connected to. |
| REMOTE_PORT | Port of the client through which the CGI script was called | The port number usually lies in a range from 1.024 upwards and is selected at random by the calling web browser. |
| REQUEST_METHOD | post or get | The method used to transfer data from the browser to the server. |
| REQUEST_URI | Path of the script, starting with the document root of the server | Also contains data transferred to the server via get. |
| QUERY_STRING | Query string | Data sent to the server as a character string, starting with a ?. |
HTTP Error Messages
The following table shows the names and error codes of the browser’s HTTP error messages as well as the corresponding HTTP error codes (for HTTP Codes see RFC 2616).
| Name | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ERR_HTTP_CONTINUE | 0x50A | Equivalent to HTTP Code 100. |
| ERR_HTTP_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS | 0x50B | Equivalent to HTTP Code 101. |
| ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_OK | 0x514 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 200. |
| ERR_HTTP_CREATED | 0x515 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 201. |
| ERR_HTTP_ACCEPTED | 0x516 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 202. |
| ERR_HTTP_NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION | 0x517 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 203. |
| ERR_HTTP_NO_CONTENT_OCTET | 0x518 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 204. |
| ERR_HTTP_RESET_CONTENT | 0x519 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 205. |
| ERR_HTTP_PARTIAL_CONTENT | 0x51A | Equivalent to HTTP Code 206. |
| ERR_HTTP_MULTIPLE_CHOICES | 0x51E | Equivalent to HTTP Code 300. |
| ERR_HTTP_MOVED_PERMANENTLY | 0x51F | Equivalent to HTTP Code 301. |
| ERR_HTTP_MOVED_TEMPORARILY | 0x520 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 302. |
| ERR_HTTP_SEE_OTHER | 0x521 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 303. |
| ERR_HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED | 0x522 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 304. |
| ERR_HTTP_USE_PROXY | 0x523 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 305. |
| ERR_HTTP_BAD_REQUEST | 0x528 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 400. |
| ERR_HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED | 0x529 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 401. |
| ERR_HTTP_PAYMENT_REQUIRED | 0x52A | Equivalent to HTTP Code 402. |
| ERR_HTTP_FORBIDDEN | 0x52B | Equivalent to HTTP Code 403. |
| ERR_HTTP_NOT_FOUND | 0x52C | Equivalent to HTTP Code 404. |
| ERR_HTTP_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED | 0x52D | Equivalent to HTTP Code 405. |
| ERR_HTTP_NOT_ACCEPTABLE | 0x52E | Equivalent to HTTP Code 406. |
| ERR_HTTP_PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED | 0x52F | Equivalent to HTTP Code 407. |
| ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_TIMEOUT | 0x530 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 408. |
| ERR_HTTP_CONFLICT | 0x531 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 409. |
| ERR_HTTP_GONE | 0x532 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 410. |
| ERR_HTTP_LENGTH_REQUIRED | 0x533 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 411. |
| ERR_HTTP_PRECONDITION_FAILED | 0x534 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 412. |
| ERR_HTTP_REQUESTED_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE | 0x535 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 413. |
| ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_URI_TOO_LARGE | 0x536 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 414. |
| ERR_HTTP_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE | 0x537 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 415. |
| ERR_HTTP_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE | 0x538 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 416. |
| ERR_HTTP_EXPECTATION_FAILED | 0x539 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 417. |
| ERR_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR | 0x53C | Equivalent to HTTP Code 500. |
| ERR_HTTP_NOT_IMPLEMENTED | 0x53D | Equivalent to HTTP Code 501. |
| ERR_HTTP_BAD_GATEWAY | 0x53E | Equivalent to HTTP Code 502. |
| ERR_HTTP_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE | 0x53F | Equivalent to HTTP Code 503. |
| ERR_HTTP_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT | 0x540 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 504. |
| ERR_HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 0x541 | Equivalent to HTTP Code 505. |
WML
This chapter describes the elements available in WML Version 1.3 and how these are interpreted by the browser. Please note that - apart from the attribute title - only those elements are described that have an impact in the browser. General attributes such as id, class or xml:lang would only be functional in case of using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). An exception is the id attribute of the <card> element used for navigation between individual cards. WMLScript does not provide access to individual WML elements.
Supported Version
The browser supports WML Version 1.3. The corresponding DTD is available - among other technical materials - from the Open Mobile Alliance.
XML Prologue
According to the specifications there must not be any characters preceding the XML prologue. The optiPoint application module’s browser, however, tolerates such characters (like the majority of other WEB browsers). It even tolerates if the entire prologue is missing.
Example for an XML prologue:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE wml PUBLIC "-//WAPFORUM//DTD WML 1.1//EN" "http://www.wapforum. org/DTD/wml_1.1.xml">
WML: Overview
The following WML elements are described depending on how the optiPoint application module supports them:
| Category | Element | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Basic structure | wml | root element |
| head | Container for <meta> and <access> | |
| meta | Meta data for the document | |
| access | Access rights for the document | |
| card | WML page | |
| templat | Container for card-spanning <do> and <onevent> elements | |
| Text structure and positioning | br | Line break |
| p | Paragraph | |
| pre | Pre-formatted text | |
| Tables | table | Table |
| tr | Table row | |
| td | Table cell | |
| Text formatting | em | Accentuation |
| dtrong | Bold | |
| b | Bold | |
| i | Italics | |
| u | Underline | |
| big | Large font | |
| small | Small font | |
| Links and Tasks | a | Hyperlink |
| anchor | Container for the tasks <go>, <prev>, <refresh> | |
| go | Hyperlink with the option of sending data | |
| prev | Back to the URL last visited | |
| refresh | Refresh | |
| noop | Cuts off the functions of <do> or <onevent> | |
| Graphics / Images | img | Embeds a graphics file |
| Events | do | Generates a softkey |
| postfield | Hands over data to the server | |
| onevent | Executes a code in case of a pre-defined event | |
| User input | input | Entry field |
| select | Selection | |
| option | Optional element | |
| fieldset | Grouping of elements | |
| Variables | setvar | Sets a variable |
| timer | Timer |
WML Basic Structure: Deck, Card
The organization of WML documents is fundamentally different from the way HTML documents are organized. In case of HTML documents, one page is loaded and displayed completely in the browser at a time. Using labeled anchors (<a name="NAME">), it can be separated into fragments that the user can select via hyperlinks. In this case the browser scrolls down/up to the correct position. An HTML page is equivalent to a file. In WML, however, the deck is the superior unit, containing one or more card elements. A WML card conforms to an HTML page insofar as it is displayed completely in the browser. The syntax for navigating between the individual cards of a deck is similar to the syntax used for navigating between HTML fragments. The technical background for this is that in case of mobile terminal devices (the main consumers of WAP pages) the latency for requesting new data from the server is relatively high.
- <wml>
- This is the root element of a WML deck. It can contain any number of <card> elements.
- <head>
- This element is a container for the specifications in the <meta> and <access> tags.
- <meta>
- This element provides various meta statements about the WML document currently loaded in the browser.
Please note that certain attributes only make sense when used in combination with others, e.g. <meta http-equiv="Cache-Control" content="nocache"/>. This results in special formats for the following statements:
http-equiv:
| Value | Value of content | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cache-Control | no-cache
max-age=time in seconds |
This combination of attributes has no impact on the browser behaviour (however, a deck is re-loaded anyway every time it is accessed). |
| Value of name | Value of content | Function |
|---|---|---|
| author keywords ... | CDATA | Using this combination, some general attributes that shall not be displayed in the browser can be included with the document. Example: name="author" content="John Doe".
The user can select any value for name and thus is free to define his own description categories. |
forua:
| Value | Function |
|---|---|
| true false | Using the boolean values true or <<t>false</tt> you can determine whether the meta statements shall be sent to the browser or not. |
- <access>
- This element defines the access rights for the WML element using the attributes domain and path. The element is supported with its specific attributes domain and path.
| Attribute | Value | Function | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Url | The value of this attribute determines from which domain the current deck may be accessed. Example: "http://www.siemens.com" | If the access is denied, the browser issues the error code 801. |
| path | Pfad | Using this attribute, the URL from which the deck can be accessed can be specified in more detail. The path statement is relative to the Document Root directory of the specific domain. Example: /wap |
- <card>
- This element provides a container for the actual content.
A WML document or deck can contain several <card> elements. A WML card is equivalent to an HTML page insofar as a WAP browser will always display only one card from a deck. Using the id attribute, you can directly jump to the individual.
| Attribute | Value | Function | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| newcontext | true false | The presetting is false. If the value is set to true, the user entries are deleted. | |
| ordered | true false | The presetting is true. This value determines that the content will be displayed in a pre-defined order. | The browser will always display the content in the predefined order, no matter whether this attribute is available and what value it is set to. |
| title | CDATA | The title is displayed in the system bar. | |
| onenterbackward | Url | This URL is accessed if the user accessed the current <card> via a <prev> task. | |
| onenterforward | Url | This URL is accessed if the user accessed the current <card> via a <go> task or via a standard hyperlink (<a href>. | |
| ontimer | Url | The URL specified in this attribute is accessed if the time set in the corresponding <timer /> element has expired. | |
| id | ID | The id attribute is necessary to make a card a target for a reference/jump. | To generate a hyperlink to a specific card, the URL statement has to contain the id together with the prefix #, e.g.: <a href="#card1"></a> |
- <template>
- The <template> element serves as a container for <do> and <onevent> elements and is positioned above the <card> level. The statements included apply to all cards of the WML document. Using the specific attributes onenterforward and onenterbackward you can determine the behaviour of the individual cards.
| Attribute | Value | Function | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| align | left | The content is displayed right-aligned. | |
| right | The content is displayed right-aligned. | The distance to the right border of the display area is bigger than the minimum distance of a line end to the right border. | |
| center | The content is displayed centered. | ||
| mode | wrap | Default setting: If the end of the display area is reached, a line break is produced. | |
| nowrap | No line break is produced. The display area is extended as required. |
- <pre>
- This element specifies that line breaks are only determined by the control characters of the character set used. If the WML code contains several consecutive blanks within <pre> tags, these will be displayed.
The browser responds to the line breaks in the WML document and also displays several consecutive blanks. Tabs are displayed as horizontal spaces only slightly wider than blanks. In addition, please note that the basic function of the tab - justification - is ignored. If a tab is inserted between two characters or strings of characters, the horizontal positioning of the haracters after the tab does not only depend on the length of the tab but also on the starting position of the tab.
Lines are wrapped automatically if they are longer than the width of the browser window. The display area is not extended by using a horizontal scroll bar. Please also note the behaviour of the browser in case a <pre> element follows a <p> element: The content of the <pre> element is separated from the content of a previous <p> element with a horizontal offset that is bigger than a normal line break.
- TBD ###
Internationalization and Special Characters
WTAI (Wireless Telephony Applications Interface)
WMLScript
Browser Error Messages
References
Reference documents
<dirlist dir="opapm"></dirlist>