OpenScape Cordless IP V2
The Wiki of Unify contains information on clients and devices, communications systems and unified communications. - Unify GmbH & Co. KG is a Trademark Licensee of Siemens AG.
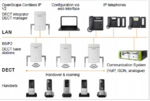
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 is the DECT over IP solution for pure and hybrid Unify IP platforms.
The radio technology used in the OpenScape Cordless IP V2 solution complies with the DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) standard. The OpenScape Cordless IP V2 solution makes the DECT standard already established for mobile voice communications also available in Voice over IP infrastructures. The entire radio range managed by the system consists of DECT IP base stations that either together form a seamless network of overlapping and synchronous radio cells or individual islands of radio signals. The size of a radio cell depends on local conditions. The connection to the Voice over IP infrastructure is made by means of the SIP protocol. This means that DECT radio cells are the perfect way to supplement SIP-capable Voice over IP systems as mobile communication solutions. DECT IP base stations support the seamless handover of existing voice connections, in other words the changeover between the radio cell and a DECT handset during a call. In addition, the roaming function is made available to mobile users, i.e. the change of radio system without an existing call.
Contents
Key Features
The entire radio range managed by the system consists of DECT IP base stations that either together form a seamless network of overlapping and synchronous radio cells or individual islands of radio signals. The size of a radio cell depends on local conditions.
DECT IP base stations support the seamless handover of existing voice connections, in other words the changeover between the radio cell and a DECT handset during a call. In addition, the roaming function is made available to mobile users, i.e. the change of radio system without an existing call.
Solution Components
The OpenScape Cordless IP V2 system solution consists of the following main components:
- Handset: DECT handsets with PN-CAP functionality
- Base station: DECT IP base station with PN-CAP/GAP functionality for the DECT handsets and IP interface with the Ethernet network
- OpenScape Cordless IP V2 software (DECT Manager and Integrator) is the central software component for:
- controlling the DECT IP base stations
- implementing the SIP/RTP interfaces in the direction of the Communication Server
- central administration and configuration of the entire OpenScape Cordless IP V2 solution
The DECT Manager SW can run either on an active DECT IP base station (small solution) or on a DECT IP base station with deactivated DECT part (medium Solution).
The Integrator SW runs either together with the DECT Manager on a base station (small and medium solution) or separate on a virtual server (large solution)
Overview
This section gives you an overview over the most important features of OpenScape Cordless IP V2.
DECT IP base station (BSIP2)
DECT IP base stations form a network of radio cells and conduct communications with the handsets. If these radio cells overlap and are synchronized, the DECT handsets can move between the radio cells with an existing voice connection. The best location for the DECT IP base stations for radio coverage in a building or site is determined by means of radio measurement. Special antennae can be used for increased radio ranges. The DECT IP base stations can be fitted with an outdoor casing to protect against inclement weather. DECT IP base stations have the complete software for DECT and IP functionality. This software does not need to be configured and administered locally on the DECT IP base stations; this can be conveniently implemented on a centralized basis by means of the OpenScape Cordless IP V2 software.
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Software (DECT Manager and Integrator)
The DECT Manager software has several functions, exists once (small and medium solution) or multiple times (large solution) in the system and can be activated on one of the DECT IP base stations.
Function: Router and protocol converter
The DECT Manager software is the interface between the IP DECT base stations on the one hand and the Communication Server on the other. It has a router and protocol converter function whereby it controls the voice connections between the Communication Server and the relevant DECT IP base station and also converts these into a data format that can be used by the DECT base stations.
Only the DECT Manager knows the DECT IP base stations with which the relevant handsets are associated; this is not apparent to the Communication Server. The DECT Manager software is a Gateway User agent for the Communication Server which manages the configured handsets. The DECT Manager software is also used to register all handsets on the Communication Server; this software administers the login procedure and the active DECT handsets.
The Integrator SW exists only once in the system and runs in small and medium solution together with the DECT Manager on one of the DECT IP base stations, in the large solution on a virtual server under VMWare.
Function: Configuration and administration interface
All administration and configuration of DECT IP base stations and OpenScape Cordless IP V2 software itself is executed by means of the web-based management of Integrator software.
Function: Synchronization management
In DECT systems with a circuit-switched connection, e.g. OpenScape Cordless Enterprise/Office systems, the synchronization information required to synchronize the base stations is derived from the UP0 connection. This is not possible in the case of the OpenScape Cordless IP V2system. However, accurate time synchronization between the DECT IP base stations is vital for a seamless call handover.
A seamless handover cluster is formed between synchronous DECT IP base stations; calls can only be handed over seamlessly in this cluster. More clusters of this type are possible for each Communication Server, however these are not synchronized with each other. Seamless handover is not possible between different non-synchronous clusters.
Synchronization via DECT (radio synchronization) In order to synchronize with another DECT IP base station via the DECT interface, a DECT IP base station must be within the overlap area of the radio cell that forms this DECT IP base station.
In addition, the DECT IP base station can be synchronized on other DECT IP base stations, which increases the availability of synchronicity in this cluster. In the event that synchronicity is lost, this DECT IP base station no longer accepts calls. After all ongoing calls on the asynchronous DECT IP base station have been ended, an attempt is made to resynchronize this DECT IP base station. Only then can new calls be made on this DECT IP base station.
Synchronization via LAN
In contrast to an air based synchronization mechanisms, synchronization via Ethernet (acc. IEEE1588, PTP Precious Time Protocol) requires less configuration.
On the other hand, great demands are made on the Ethernet characteristics like symmetry, packet loss, delay, jitter (variance of delay). Therefore special requirements regarding the Ethernet components (especially the Ethernet switches used) have to be considered. Exceeding of limits (especially of jitter) will lead to loss of synchronization, which will finally lead to a resynchronization process. During this process the belonging base stations are unable to establish telephony connections.
The LAN synchronization solely uses a star shaped topology. Maximally one base station serves a Synchronization Master, all other base stations which participate at the synchronization serve as Synchronization Slaves.
The main advantages of synchronization via LAN are:
- more flexibility in the location of the DECT IP base station - no need to built synchronization chains as with synchronization via DECT,
- less DECT IP base stations are required, because the overlapped area of DECT IP base station is less,
- configuration of DECT IP systems is simplified, because all DECT IP base stations can be synchronized to only one synchronization master
Communication Interfaces
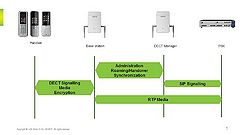
The figure contains an overview of the protocols used between the DECT handsets, DECT IP base stations, OpenScape Cordless IP V2 software and the Communication Server.
The following is an overview of the communication relationships used in the solution:
DECT handset - user: DECT handset, with alternative headset or Bluetooth headset
DECT handset – DECT IP base station (BSIP2): A call can be handed over seamlessly between the DECT IP base stations.
DECT IP base station (BSIP2) – DECT IP base station (BSIP2): Accurate time synchronization between the DECT IP base stations is vital for a seamless call handover.
DECT IP base station (BSIP2) – DECT Manager SW: The DECT IP base stations all communicate with the DECT Manager software; the signaling data is transported in this connection. The connection protocol between the DECT IP base stations and the DECT Manager Software is system specific; it is IP-based and uses UDP packages in both directions.
DECT Manager software – Communication Server: The SIP protocol between the DECT Manager software and Communication Server is standards-based Integrator software - time server: A time server is not absolutely necessary. The time information is used to display this when the DECT handset is idle and to file the caller list with correct data. The Communication Server can also be managed as a time server.
Features that can be made available on the Supported Devices
- outgoing/incoming calls
- calling line identity presentation (CLIP)
- calling name identity presentation (CNIP)
- hold – including music on hold while a caller is waiting
- consult
- toggle
- forward when busy, no reply and always
- attended/unattended transfer
- 3 party conference
- ringer tone mute by incoming calls
- call reject
- time and date display at idle screen
- internal/external call ringer differentiation
- missed call list for incoming calls on a DECT handset, including MWI signaling
- received call list
- Voice Mail list incl. MWI signaling
- DTMF transmission
- Integration of DECT handsets into Basic-MULAP-groups
- group call possible between DECT handset and Unify system phones (both phones ring when an incoming call is received; when the call is answered using one of the two phones, the other phone stops ringing)
- Second Line incl. Call Waiting Tone
- Call Completion
- SIP Survivability
- Directory options:
- corporate directory: LDAP access via DECT handset
- private directory: handset internal telephonebook
Features per supported Platform:
You can find here a detailed overview of the features with the different platforms.
Connectable Devices
Supported Platforms
Supported DECT handsets
- OpenStage SL4 professional
- Gigaset S4 professional
- OpenStage M3 family
- OpenScape DECT Phone S5
- OpenScape DECT Phone SL5
Diagnostics Requirements
The following info is required for call and handset related problems:
- The detailed, actual problem description including the following info
- The statistical distribution of the problem
- The current site plan (position plan) of the base stations
- A current network deployment plan including the following info as picture
- The radio coverage at the location where the problem occurs
- A Wireshark trace recorded at a mirror port of the IWU of the BSIP
- Attach also the internal diagnosis data from the PBX
- PSR files if PSR required
Installation Checklist
For any deployment the installation checklist (see below in the documents section) must be used and filled out. In case of support the installation checklist must be added to the ticket.
Technical Data
Features of the DECT IP Base Station (BSIP2)
DECT Features
- Support for the maximum number of DECT channels: 120
- DECT GAP support (see comment in section 1.1.2.)
- Extended scope of features for the supported DECT handsets (PN-CAP standard)
- Support for fast antenna diversity
- Connector for external antennas
Note: In the documentation part you can find two slide sets with recommendations and technical information for external antennas from Huber&Suhner.
Ethernet Features
- Ethernet 10/100 Base T connection
- Power-over-Ethernet Power Class 2 (IEE802.3af)
- Software download/update available
- VLAN
- DHCP
- Quality of Services in the network:
- Layer 2 prioritization (802.1p/q)
- Layer 3 prioritization (ToS, DiffServ)
- Echo cancellation
- Integrated https server for accessing the solution's Web-based management
- Supported Codec’s: G.711, G.729, G.722 wideband, G.726 for the DECT voice packages
Additional Features if the DECT Manager Software has been activated on the DECT IP base station
On the Communication Server route, this DECT IP base station also offers:
- SNMP V2
- SIP via UDP, TCP and TLS (step 2)
Miscellaneous
- The outdoor casing already familiar from the OpenScape Cordless Enterprise base station BS5 and BSIP1 can be used as the outdoor casing. If needed, a mast mounting kit can be ordered in addition.
Customer Requirements and Functional Boundary Conditions
System Configuration
Scenarios can be implemented in which several OpenScape Cordless IP V2 systems can be run on each Communication Server. In these cases, a seamless handover between the various clusters formed from synchronous DECT IP base stations is not possible.
1st scenario – DECT Manager and Integrator SW run on one of the DECT IP base stations (small solution)
All DECT IP base stations always also have the functionality of the DECT Manager and Integrator software. This means, in principle, that every DECT IP base station can assume the function of the DECT Manager and Integrator SW in addition to the actual DECT functionality. The DECT Manager and Integrator SW must be activated to enable the DECT IP base station to assume this function.
Because of the available hardware resources on the DECT IP base station, the following system restrictions apply in this release step:
- up to 10 DECT IP base stations
- up to 10 parallel calls
- up to 50 handsets can be registered
2nd scenario – DECT Manager and Integrator SW run on a dedicated BSIP2 with deactivated RF part
The DECT Manager and Integrator SW run on a dedicated BSIP2, on which the DECT part is deactivated.
The following system restrictions apply in this release step:
- up to 60 DECT IP base stations
- up to 60 parallel calls
- up to 250 DECT handsets ca be registered
3rd Scenario – Integrator SW runs on a virtual server and controls more than one DECT Manager
The integrator SW runs centrally on a virtual server and controls more than one DECT Manager. The DECT Manager SW runs either on a BSIP2 with active DECT part (than up to 10 BSIP2 can be controlled) or on a dedicated BSIP2 with deactivated DECT part (and up to 60 BSIP2 can be controlled).
The following system limits apply in this scenario:
- up to 10/60 base stations per DECT Manager
- up to 10 DECT Managers in a handover domain/site
- up to 100 DECT Managers per system
- up to 6.000 parallel calls per system
- up to 20.000 DECT handsets per system
3rd Scenario – Integrator SW is running on a dedicated BSIP2
The integrator SW runs on a dedicated BSIP2 (with deactivated radio part and DECT manager SW).
The following system limits apply in this scenario:
- up to 10/60 base stations per DECT Manager
- up to 4 DECT Managers per system/handover domain
- up to 240 parallel calls per system
- up to 800 DECT handsets per system
You will find details in the corresponding sections of the Service Manual.
Network Requirements
If Voice over IP is to be integrated in a network environment, it is necessary to create conditions so that the voice connections can be operated smoothly by means of IP networks. The IP network must meet the general requirements for a VoIP network in relation to delays, losses and guaranteed service quality features. This means that network analysis must be performed during the pre-sales phase or, alternatively, the customer must undertake to observe the required IP network criteria.
Further information can be found in the respective section of the service guideline.
In addition, the following special conditions must be met between the DECT IP base stations and the corresponding DECT Manager in the IP network:
- these must be part of the same Ethernet segment; neither layer 3 routing via an IP router or Network Address Translation (NAT) are supported
- at least 2 priority classes according to IEEE 802.1 p/q are required in the VoIP network in order to prioritize the voice data
- Use of 100 Mbps full duplex for all switched LAN ports
Otherwise delays occur in the IP network, leading to synchronization and voice quality problems on the DECT handsets.
Very import requirements in case LAN synchronization is used
- The number of L2 Ethernet switches between the Synchronization Master and a Synchronization Slave has to be as low as possible.
- Only enterpirse class switches are supported.
- The packet flow in the network must be symmetric and jitter must be minimal.
- VLAN based prioritisation of LAN packets could be a fruitful measure to minimize packet delay and its jitter.
- Jitter has to be below an average value of 500ns.
- PTPv2 is defined in the standard IEEE 1588-2008
The PTPv2 datagrams are (partially) sent as multicast and transported via UDP on IPv4. Multicast destination address: 224.0.1.129 UDP/PTP2 Ports 319/320 Multicast destination address: 239.0.0.37 UDP/propritaey Ports 21045/21046
- IGMP snooping is supported by OSCIPv2 and should be supported by the switch, so that the switch can be automatically configured on which ports the multicast packets should be sent to.
Analysis of the Building/Campus (Site Survey)
When the DECT network involves approximately 3 DECT IP base stations, a site survey must be carried out on the customer environment. This is particularly the case if:
- several floors or buildings are to be covered with DECT
- the solution will have to coexist with other DECT installations
- other radio-intensive devices are operated in the environment.
Prior to any deployment service training for OpenScape Cordless IP V2 has to be done by service technicians, engineers and consultants. In the indirect channel our sales partners have to build up know-how using the offered trainings as well.
In case of replacement of an existing DECT or DECT IP solution (i.e. when base stations from other vendors or Unify BS4 are replaced by BSIP1), a new site survey is mandatory. Each base station type behaves differently regarding HF characteristics, so a simple replacement may cause coverage problems.
Documentation
Information
Documentation
For the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) see -> Declarations_of_Conformity
-
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Administration Documentation english issue6
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Administration Documentation english issue6 -
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Service Documentation english issue7
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Service Documentation english issue7 -
 Service Guideline Mitel OpenScape Cordless IP V2
Service Guideline Mitel OpenScape Cordless IP V2 -
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2, Security Checklist, Issue 4 (1)
OpenScape Cordless IP V2, Security Checklist, Issue 4 (1) -
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Installation Checklist english
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 Installation Checklist english -
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2 External Antennas Overview english
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 External Antennas Overview english -
 OpenScape Cordless IP V2 External Antennas Technical Information english
OpenScape Cordless IP V2 External Antennas Technical Information english
Platforms:
Handsets: